Journal of Bionic Engineering (2025) 22:1381–1399https://doi.org/10.1007/s42235-025-00693-w
Halochromic Highly Sensitive Bio-polymeric Film Composed from Polyvinyl Alcohol and Monomeric Euphorbia Pulcherrima Anthocyanins Bracts for the Detection of Freshness of Minced Meat
Huda Ahmad Alamer1 · Mohamed N. Saleh2 · Menna Allah M. Youssef2 · Mohamed El-Bana2 · Reham M. Kamel3 · Mohamed M. El-kholy3 · Enas El. Fadly4 · Mohamed Abdelbaset Salama2 · Mohamed Abdin2
1 Department of Physical Sport Sciences, College of Sport Sciences and Physical Activity, Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
2 Agricultural Research Center, Food Technology Research Institute, Giza 12611, Egypt
3 Agricultural Engineering Research Institute, Agricultural Research Center, Giza 12611, Egypt
4 Dairy Sciences Department, Faculty of Agriculture, Kafrelshiekh University, Kafrelshiekh 33511, Egypt
Abstract
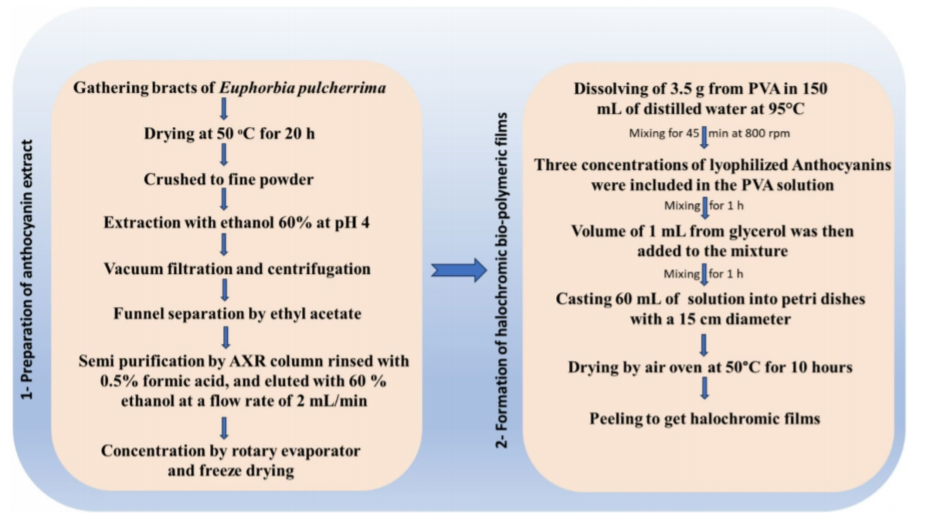
Polyvinyl alcohol was used as a halochromic carrier material for anthocyanins extracted from bracts of Euphorbia pulcherrima. Including anthocyanins in halochromic carrier improved the thickness, solubility, swelling capacity, water vapor permeability, antioxidant properties, and tensile strength of the films. The high levels of anthocyanins decreased the water contact angle to 60.48°. Adding anthocyanins to films altered the color of halochromic films in response to exposure to ammonia emission or pH changes, allowing for the creation of smart sensors. The artificial biosensors altered the color linked to decreased freshness of the minced meat primarily because of ammonia generation and pH changes as the meat decays. One key point is that halochromic sensors can biodegrade and break down under simulated environmental conditions in just 30 days. In general, the created intelligent biosensors could be utilized as halochromic materials to detect the initial stages of food spoilage.
Keywords Halochromic films · Minced meat · Euphorbia pulcherrima anthocyanins bracts
Copyright © 2025 International Society of Bionic Engineering All Rights Reserved
吉ICP备11002416号-1









